Diabetes is a chronic disease that occurs when the body doesn't produce enough insulin or can't use it properly:
Type 1 diabetes
The pancreas produces little or no insulin because the immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells.
Type 2 diabetes
The body either doesn't produce enough insulin or the cells don't respond well to insulin. This is the most common type of diabetes and usually occurs in adults.


Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a condition where the pressure of blood in the blood vessels is consistently too high. It's a serious medical condition that can increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, eye problems, and other health issues.
Lifestyle Changes:
• Eat a healthy diet & Limit alcohol, Don't smoke.
• • Manage stress.
• Maintain a healthy weight, Get more exercise.
• Practice good sleep habits & Try slow, deep breathing.
A thyroid disorder is a medical condition that affects the thyroid gland, which is located in the neck and produces hormones that regulate other organs. Thyroid disorders can cause the thyroid to produce too much or too little of these hormones.
Symptom: Changes in Energy or Mood
Thyroid disorders can have a noticeable impact on your energy level and mood. Hypothyroidism tends to make people feel tired, sluggish, and depressed. Hyperthyroidism can cause anxiety, problems sleeping, restlessness, and irritability.
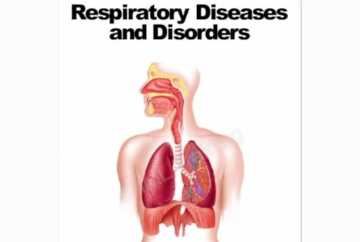
A respiratory illness is a disease that affects the lungs or other parts of the respiratory system.
Infection
Respiratory tract infections (RTIs) can be caused by viruses, like colds, or bacteria, like pneumonia.
Smoking
Smoking tobacco or breathing in secondhand smoke can cause respiratory illnesses.
Air pollution
Breathing in radon, asbestos, or other forms of air pollution can cause respiratory illnesses.
Asthma is a chronic lung disease affecting people of all ages. It is caused by inflammation and muscle tightening around the airways, which makes it harder to breathe. Symptoms can include coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath and chest tightness. These symptoms can be mild or severe and can come and go over time.
Symptoms
Symptoms include coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness. Symptoms can vary in severity and come and go. When symptoms worsen, it's called an asthma attack.


COPD, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, is a condition caused by damage to the airways or other parts of the lung. This damage leads to inflammation and other problems that block airflow and make it hard to breathe. COPD can cause coughing that produces large amounts of a slimy substance called mucus .
What is COPD caused by?
Smoking and air pollution are the most common causes of COPD. People with COPD are at higher risk of other health problems. COPD is not curable but symptoms can improve if one avoids smoking and exposure to air pollution and gets vaccines to prevent infections.
Cardiac disease, also known as cardiovascular disease (CVD), is a general term for a group of disorders that affect the heart and blood vessels.
Some types of CVD include:
• Coronary heart disease: A disease of the blood vessels that supply the heart muscle. It's often caused by plaque buildup from cholesterol, which can block blood flow.
• Rheumatic heart disease: Damage to the heart muscle and valves caused by rheumatic fever.
• Congenital heart disease: Birth defects that affect the heart's structure and function.
• Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism: Blood clots in the leg veins that can move to the heart and lungs.

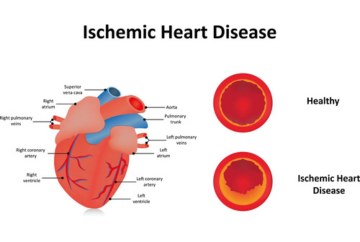
Ischemic heart disease, also known as coronary artery disease or coronary heart disease (CHD), is a heart condition that occurs when the heart's blood supply is reduced due to narrowed coronary arteries
Causes A buildup of plaque, a fatty material and cells, in the coronary arteries is the most common cause of ischemic heart disease. The plaque can obstruct blood flow, or it can rupture and cause a clot to form.
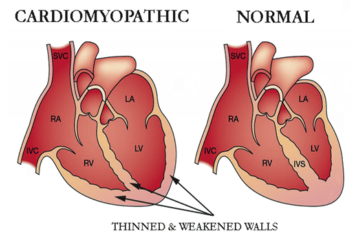
Any disorder that affects the heart muscle is called a cardiomyopathy. Cardiomyopathy causes the heart to lose its ability to pump blood well. In some cases, the heart rhythm also becomes disturbed. This leads to arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats).
Symptoms:
Early on, there may be no or few symptoms. As the disease progresses, symptoms may include shortness of breath, fatigue, swelling of the legs, dizziness, fainting, or chest pain.
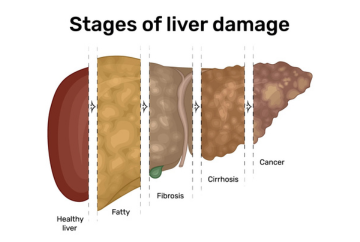
Liver disease refers to a number of conditions that can prevent the liver from functioning properly.
Viruses
Hepatitis A, B, and C are all examples of viral liver diseases.
Drugs and alcohol
Liver disease can be caused by taking too many drugs or drinking too much alcohol.
Inherited conditions
Hemochromatosis and Wilson disease are examples of inherited liver diseases.
Kidney disease occurs when the kidneys are damaged and can't filter blood properly.
Chronic kidney disease (CKD)
A condition that develops over time due to other conditions that strain the kidneys. Common causes include diabetes, high blood pressure, and kidney infections.
Kidney stones
A common and painful kidney disease that can be caused by dietary substances or not drinking enough fluids.
Polycystic kidney disease
An inherited condition that causes fluid-filled cysts to grow in the kidneys.

Infectious diseases are caused by harmful organisms that enter the body from outside, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites. They can be transmitted in many ways, including through contaminated food, water, body fluids, or the air.
Some types of CVD include:
• Bacterial diseases: Strep throat, urinary tract infections, and tuberculosis are caused by bacteria. Most bacterial infections are treated with antibiotics.
• Viral diseases: The common cold, AIDS, and COVID-19 are caused by viruses.
• Fungal diseases: Ringworm, athlete's foot, and other skin diseases are caused by fungi.
• Parasitic diseases: Malaria is caused by a parasite transmitted by mosquito bites.
Viral Bacterial, Parasitic fungus, and viral infections can be aggressive life-threatening infections or nonhostile relatively mild short-term infections. In response to all infectious agents, the body generates antibodies or generates resistance to infection agents. In all cases, bacteria, fungi, and viruses infect one cell or one tissue and then start to spread around the body infecting multiple other cells or tissues, in some cases killing humans. One common symptom of most bacterial, fungal, and virus infections is fever.

Critical care is a branch of medicine that provides medical care for patients with life-threatening injuries or illnesses. It's usually provided in an intensive care unit (ICU), a specialized hospital ward that's staffed with specially trained healthcare professionals.
Critical care involves:
• 24-hour care: A team of specially-trained healthcare providers, including physicians and nurses, provide constant care.
• Monitoring: Sophisticated monitoring equipment is used to constantly monitor vital signs.
• Specialized treatments: Patients receive specialized treatments.
A neurological disorder is a condition that affects the brain, spinal cord, or nerves, which control how the body works.
Symptoms:
• Paralysis or muscle weakness
• Poor coordination, Loss of sensation.
• Seizures, Confusion, Pain, Altered levels of consciousness.
• Problems with memory, senses, or mood.

The recommended adult vaccines depend on your age, health history, and other factors. Some vaccines that may be recommended for adults.
include:
• Tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis (Tdap or Td):Adults between 18 and 64 should get a booster dose every 10 years, or a dose of Tdap instead of Td.
• Influenza: Adults should get an annual dose of the inactivated or recombinant influenza vaccine.
• Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV): Adults should get an annual dose of the RSV vaccine.
Chronic pain management is a combination of treatments that aims to reduce pain and improve quality of life. Since chronic pain is rarely completely eliminated, treatment goals often focus on reducing pain and preventing it from interfering with daily life.
Chronic pain management can include:
• Medications
• Lifestyle changes
• Therapies
• Self-management activities
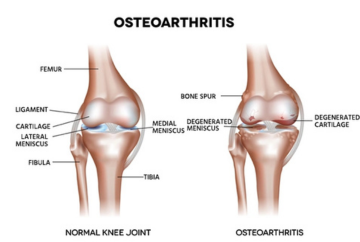
Osteoarthritis, also known as OA, is a degenerative joint disease that causes pain, stiffness, and swelling. It's the most common type of arthritis and affects the joints in the hands, knees, hips, neck, and lower back.
Symptoms:
• Pain: Pain when using the joint, especially during or after movement.
• Stiffness: Joint stiffness, usually in the morning or after resting.
• Swelling: Swelling in and around the joint.
• Other:Tenderness, loss of flexibility, grating sensation, bone spurs, clicking or popping sound when a joint bends.
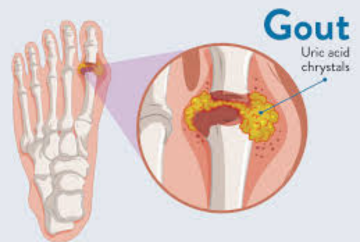
Gout is a type of arthritis that causes recurring attacks of pain, swelling, redness, and tenderness in the joints
Symptoms
Pain from gout usually comes on quickly, reaching its worst within 12 to 24 hours. The affected joint may feel hot and tender, and the skin may appear shiny.
Causes
Gout occurs when urate, a substance in the body, builds up and forms needle-like crystals in the joints. This can be caused by eating too many foods high in purines, such as red meat, organ meats, and certain seafoods.
Depression and anxiety are different mental health conditions, but they often occur together.
Depression:
• Feeling irritable or restless
• Having trouble sleeping
• Eating more or less than usual
• Feeling guilty, worthless, or helpless
• Thinking about suicide or hurting yourself
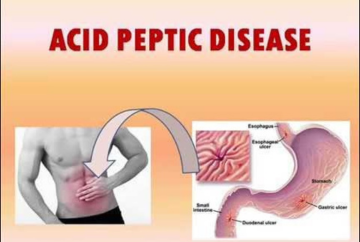
Acid peptic disorder (APD) is a group of conditions that occur when the stomach's protective lining is damaged or there is too much acid or pepsin in the stomach or duodenum.
Symptom of APD include:
• Heartburn, Abdominal pain
• Nausea, Vomiting
• Loss of appetite, Weight loss
• Passing blood in stool

Functional gastrointestinal (GI) disorders are a group of conditions that affect how the digestive tract functions.
Symptoms
Common symptoms include abdominal pain, bloating, constipation, diarrhea, gas, and nausea.
Causes
These disorders can be caused by a number of factors, including changes in the brain's processing of pain signals from the gut, or by changes in the movement of the digestive system. Other causes include a diet low in fiber, stress, or certain medications.
Cholesterol disorders are conditions that cause high levels of cholesterol in the blood.
• Hypercholesterolemia Also known as high cholesterol, this is the most precise medical term for high blood cholesterol
• Hyperlipidemia A general term for elevated lipid levels in the body, which can include hypercholesterolemia.
• Familial hypercholesterolemia A genetic condition that's passed down through families and can cause symptoms like fatty skin deposits, cholesterol deposits in the eyelids, and chest pain.

Ischemic heart disease, also known as coronary heart disease (CHD) or coronary artery disease, occurs when the heart muscle doesn't receive enough blood and oxygen. This is usually due to a buildup of plaque in the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart.
Symptoms of ischemic heart disease include:
• Chest pain or pressure, Fast or irregular heartbeat
• Pain in the neck, jaw, shoulder, or arm
• Shortness of breath, especially during exercise
• Sweating, Feeling full, indigestion, or a choking feeling
• Nausea or vomiting, Feeling lightheaded, dizzy, very weak or anxious